by Deac Jones | Mar 27, 2024 | News
The agriculture market has always been challenging, and maybe particularly so now, with pressures from declining market prices, the availability and cost of labor, new regulations, water restrictions, etc. Crop input prices are on the rise and regulations are restricting what growers can do going forward. Bottom line: Growers must find new ways to be successful.
Technology in agriculture, like in most parts of our lives, has changed how we do things and, maybe more importantly, enabled us to measure what we had only presumed or speculated about in the past. Back in 2008, Andaman Ag began introducing biological products to the market. It wasn’t the most receptive audience at that time. But while working overseas, I witnessed the benefits of biological products firsthand. One of the key takeaways was their ability to improve growers’ Return on Investment, or ROI, over time.

by Deac Jones | Feb 15, 2024 | News
Plant metabolism basically can be divided into primary metabolism, which encompasses reactions and pathways vital for survival, and secondary metabolism, which fulfills a multitude of important functions for growth and development, including the interaction of the plant with environmental stresses.

by Deac Jones | Nov 6, 2023 | News
The more we learn about fungi, the more we understand what an important role they perform in our ag work and the potential they have to deliver more significant positive impacts to the planet, including the agricultural industry.

by Deac Jones | Aug 17, 2023 | News
People ask me how I define regenerative farming and I have one simple answer: it’s all about sequestering more carbon in our soils. Soil is the largest carbon store on Earth—holding more carbon than all plants and our atmosphere put together. And contrary to what was previously believed, it now appears that a considerable amount of this carbon—more than 50%—is introduced to the soil via the remains of dead microorganisms.
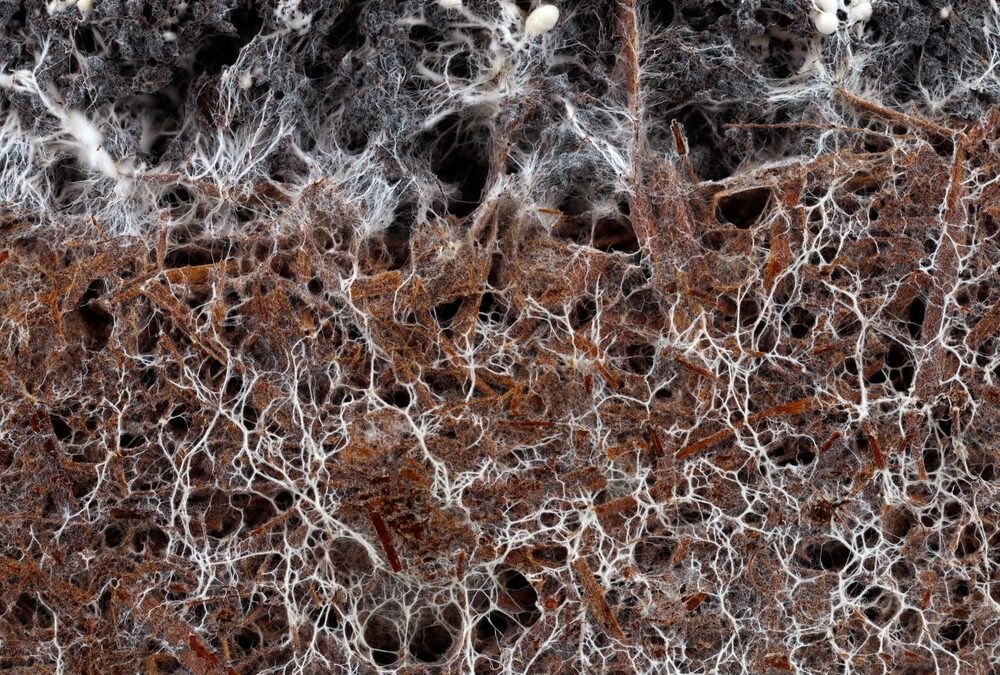
by Deac Jones | Jul 26, 2023 | News
Plants and fungi struck a deal way back when. More than 400 million years ago, plants began trading sugar (carbon) made from sunlight for some of the soil nutrients gathered by mycorrhizal fungi. Nearly 90% of all land plants are now part of this arrangement, so scientists have estimated that the amounts of carbon flowing through underground fungi must be significant. However, they didn’t realize how much carbon was in the system until now.